Accessing Zetaris through Rest API
This article shows users how to carry out Zetaris commands using the Zetaris secure API
Import the Collection and Environment Variables
To start the usage of this API , it is recommended to download the Postman collection.
Once logged into the postman application and within a workspace click on the ![]() collections widget as seen on the right.
collections widget as seen on the right.
Then click on the  button and then click on the
button and then click on the  button. Navigate to where the collection and environment files are downloaded and select them both.
button. Navigate to where the collection and environment files are downloaded and select them both.
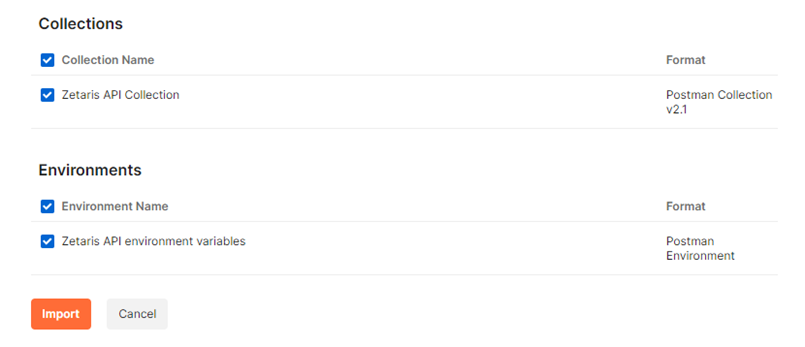
Ensure that the collection and environment variable is selected, as seen below, and then click on  .
.
Understanding the Environment variables for Postman
Currently the API collection utilises the following environment variables:
|
Variable |
Description |
|
refreshToken |
The refresh token is a token generated when logging into the API. This token will be used to regenerate the idToken |
|
idToken |
The id token is a bearer token generated when logging into the API which will be used for authorisation in future calls |
|
url |
The url is the users API URI. i.e., api.zetaris.app.com |
|
targetRole |
The numerical identification for the role being targeted. |
|
resourceTypeDQ |
Variable store the string for the Data Quality reference. |
|
emailAdmin |
Username of the user |
|
operationTypeRead |
Variable stores the String for Read permissions, “Read” |
|
resourceTypeVD |
Variable store the string for the Virtual Data Mart reference. |
|
targetAccount |
For users with access to the Data Access features. Will target a specific users account to get/update information. |
|
requestId |
Request ID is the uuid required within the header when making API calls |
|
requestTypeSS |
Variable store the string for the Schema Store reference. |
|
requestTypeDC |
Variable store the string for the Data Catalog reference. |
|
operationTypeWrite |
Variable stores the String for Write permissions, “Write” |
|
resourceTypeNDP |
Variable store the string for the NDP Fabric Builder reference. |
|
defaultAdminPassword |
This is the API users’ password. |
|
pipelineContainerId |
The numerical id of a users’ Data Pipeline Container resource. |
|
pipelineRelationId |
The numerical id of a users’ Data Pipeline resource. |
|
DataMartId |
The numerical id of a users’ Data Mart resource. |
|
DataSourceId |
The numerical id of a users’ Data Source resource. |
|
DataSourceRelationId |
The numerical id of a users’ Data Source Table resource. |
|
tag |
An alphanumerical string to tag some resources. |
|
queryToken |
The query token is generated when a user makes an API call to query a datasource or execute a pipeline. This token is required when paginating between results. |
|
oidcid |
The id of the users SSO configuration. |
|
uid |
The uid is required to configure SSO. i.e., Zetaris |
Changing your Environment Variables
In the top right corner of the postman window, click on  to view the environment variables.
to view the environment variables.
Scroll down and edit the following variables.
|
Variable |
Current Value |
|
url |
<The Zetaris instance you are using> |
|
emailAdmin |
<your registered email with SAAS> |
|
defaultAdminPassword |
<password for your registered account with SAAS> |
Login
Once the above variables have been saved. Open the Auth folder within the collection select the Login request.
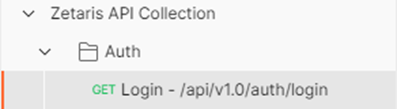
Click on to send the API request.
to send the API request.
The response returned will contain an identification token and refresh token as mentioned earlier. An example output can be seen below.
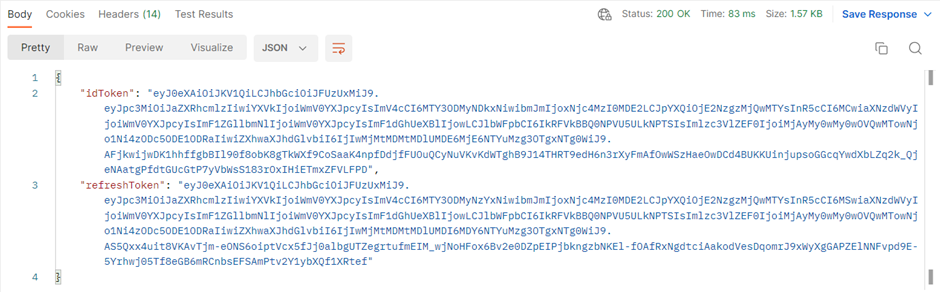
You will not need to copy the idToken or the refreshToken to the environment variables as they are automatically assigned to their respective environment variables due javascript located in the Tests tab as seen below.

Querying your Data
Running a Query
Within the collection open the folder DBQuery and select the OpenSqlQuery request.
Navigate to the Body Tab where you will see the following.
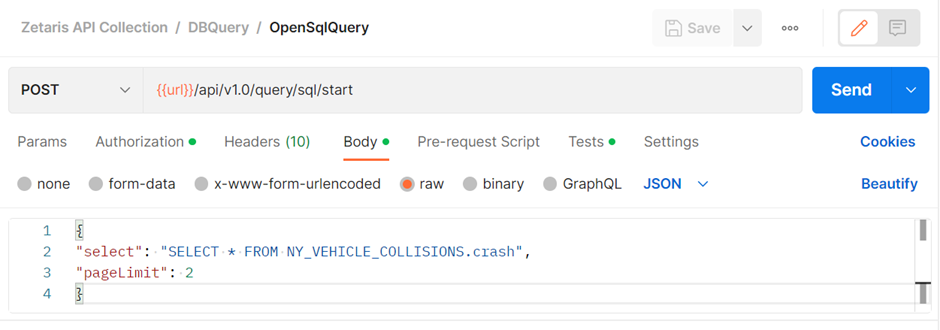
If you do no see the above JSON within the body, select raw and ensure JSON is selected. Then copy the below snippet and add it to the body.
{
"select": "SELECT * FROM NY_VEHICLE_COLLISIONS.crash",
"pageLimit": 2
}
One thing to note is that the pageLimit refers to the number of items returned per API call and has a range of 1 – 100.
To run the query, click on  . In the response section of Postman, you will see a JSON payload containing the following.
. In the response section of Postman, you will see a JSON payload containing the following.
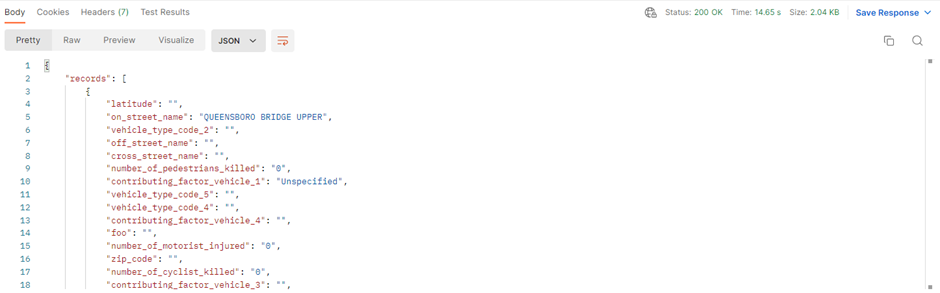
You will not need to copy the queryToken over to the environment variables as it will be automatically added to the environment variables.
Paginate a Query
Within the collection open the folder DBQuery and select the PageSqlQuery request.

Navigate to the Params tab, where you will see the following key value pairs.
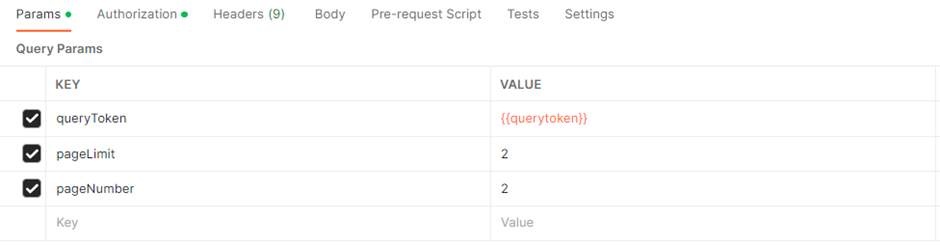
Place the values in your environment are the same as above.
To run the query, click on . In the response section of Postman, you will see a JSON payload containing the following.
Close a Query
Within the collection open the folder DBQuery and select the CloseSqlQuery request.

Within this request you will see the following:
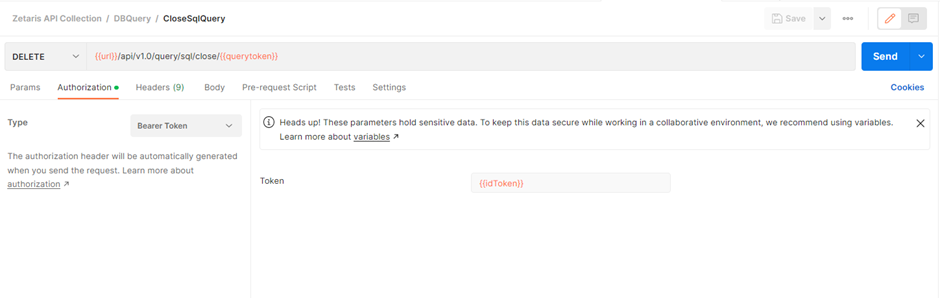
This will remove the cached query information from the server to save memory and resources.
Click on  . You will receive a response status of 200 which indicates that the query was successfully closed on the server.
. You will receive a response status of 200 which indicates that the query was successfully closed on the server.